Navigation is a complex and complex art, especially at sea, where sailors and sailors rely on a variety of tools to guide their ships. An important factor in navigation is the Earth’s magnetic field, which affects the behavior of the compass needle. Isogonic line, a term familiar to navigators, play an important role in understanding changes in magnetic declination around the world. In this comprehensive blog, we explore the concept of Isogonic line, examining what they are, how they affect navigation, and why they are so important to sailors.
Understanding Isogonic Line
Before we get into the Isogonic line, let’s lay the foundation by understanding magnetic declination. Magnetic declination is the angle between magnetic north (the direction the compass points) and true north (the direction along the Earth’s axis of rotation toward the North Pole). This angle is not constant and varies depending on geographic Location.
Properties of Isogonic Line
To truly understand the meaning of the Isogonic line, it is important to first understand the concept of magnetic declination vessel’s type. Magnetic declination represents the angle between magnetic north (the direction your compass points) and true north (the direction toward the North Pole along the Earth’s axis of rotation). This angle is not constant and varies depending on the geographical Location of the observer.
Elucidating Isogonic Line
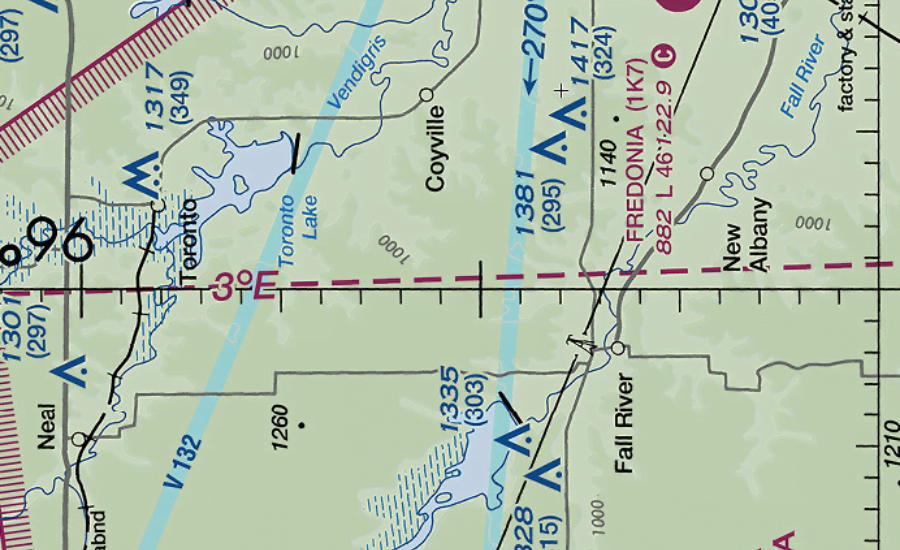
Isogonic line appear on a map as a representation of the magnetic declination of various locations on the Earth. These lines connect points of equal magnetic declination and produce a graphical representation of the spatial distribution of this important navigation parameter. Simply put, the Isogonic line acts as a vessel’s type, showing how much the magnetic north deviates from the true north at various geographic points.
What is an Isogonic Line?
An isometric line is a line on a map that connects points of the same magnetic declination. These lines are graphical representations of the magnetic declination of a particular region or area; simply put, they show how far the magnetic north deviates from the true north at various locations.
Importance of Isogonic Line in Navigation
Navigation Accuracy
Isogonic line are essential for navigators who use magnetic compasses. These provide a visual representation of magnetic declination, allowing sailors to adjust compass readings for more accurate navigation.
Course Planning
When planning a course, sailors must consider the difference between magnetic north and true north. Isogonic line aid in route planning and help mariners predict and adapt to variations in magnetic declination as they traverse different regions.
Avoid Navigation Errors
Failure to take magnetic declination into account can lead to navigation errors. By referencing maps that include the Isogonic line, sailors can avoid deviations from their planned course and increase navigation accuracy. Factors Affecting Magnetic Declination To understand the importance of Isogonic line, it is important to understand why magnetic declination changes.
Several Factors Influence These Variations.
Geographical Location
Magnetic declination is affected by the vessel’s position on the Earth’s surface. Different locations have different angles between magnetic north and true north.
Change Over Time
Earth’s magnetic field is not static. It may change over time. Secular change refers to slow and continuous changes in the Earth’s magnetic field that affect the magnetic declination.
Movement of Magnetic Poles
Movement of magnetic poles contributes to variations in magnetic declination. As the magnetic poles move, the angle between magnetic north and true north also changes.
Local Magnetic Effects
Local magnetic anomalies, such as the presence of iron ore deposits or geological formations, can cause variations in the magnetic declination.
Isometric Drawings Use
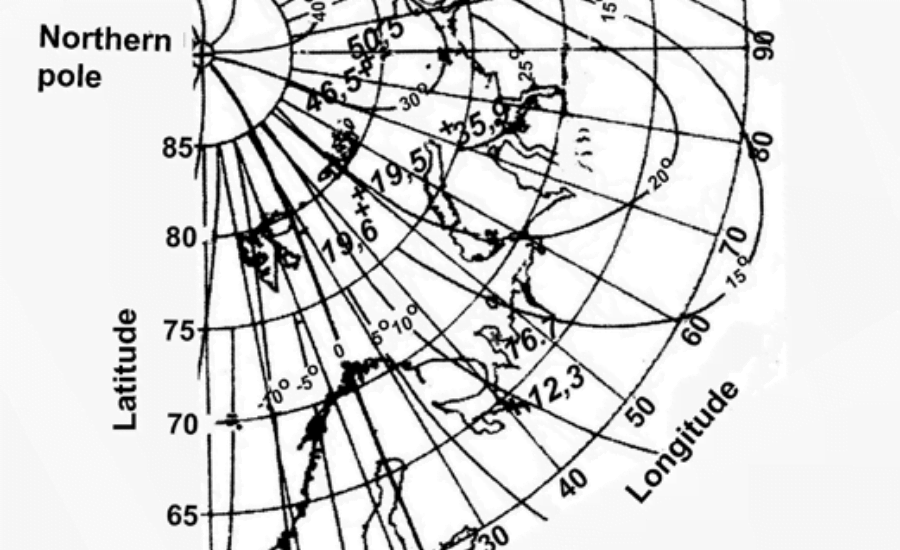
Navigators often refer to isometric maps and nautical charts to obtain information about the magnetic declination of a particular area. These charts display Isogonic lines at regular intervals, allowing sailors to interpolate declination values between the lines.
Representation of Isolines
Isolines are isolines that connect points of the same magnetic declination. The lines usually form a pattern similar to contour lines on a topographic map.
Map Legend
Isometric maps include a legend that shows the value of the magnetic declination along the line. Navigators can rely on these legends to determine the expected declination at various locations.
Adjusting Compass Readings
Sailors use isometric maps to adjust compass readings based on the expected magnetic declination in a particular area. This ensures that the navigation heading is true north.
Conclusion
In summary, Isogonic lines are a fundamental tool for navigators and provide valuable information about the variation of magnetic declination in different regions. A solid understanding of these lines is critical to accurate navigation and helps sailors reconcile discrepancies between magnetic north and true north. As technology continues to advance and electronic navigation systems become more widely used, a solid understanding of the principles behind the Isogonic line remains important for maritime professionals navigating the vast open seas. Whether navigating the ocean or mapping coastal waters, mariners continue to rely on the age-old concept of Isogonic line to navigate accurately and safely, ensuring safe and accurate navigation to their destination.









