A Comprehensive Guide to Dual Fuel Marine Engines and Their Benefits
Dual fuel marine engines have emerged as a promising solution to the growing demand for cleaner, more efficient, cost-effective propulsion systems in the maritime industry. By combining the power of traditional marine diesel oil (MDO) or marine gas oil (MGO) with cleaner fuels like liquefied natural gas (LNG), these engines offer a compelling alternative to conventional propulsion systems.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of dual fuel marine engines, exploring their technology, benefits, and applications. By understanding the intricacies of these engines, we can appreciate their potential to contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly maritime sector.
1. What Are Dual Fuel Marine Engines?
Dual fuel marine engines are designed to operate on a combination of two different fuels, typically MDO/MGO and LNG. This innovative approach allows for greater flexibility and adaptability in marine operations. The engines incorporate specialized fuel management systems that can seamlessly switch between fuels based on various factors, including fuel availability, economic considerations, and environmental regulations.
Types of Fuels Used
- Marine Diesel Oil (MDO) and Marine Gas Oil (MGO): These traditional marine fuels provide the necessary power and performance for marine operations. They are widely available and well-established in the industry.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): LNG offers significant environmental benefits as a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. Compared to MDO and MGO, it emits significantly lower levels of greenhouse gases, sulfur oxides, and nitrogen oxides. Additionally, LNG is often more cost-effective than traditional marine fuels, especially in regions with abundant natural gas resources.
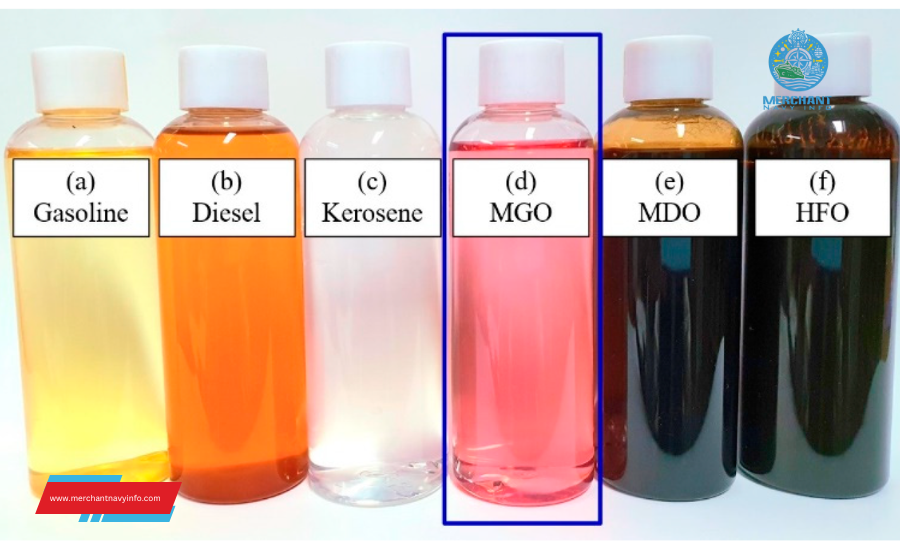

Comparison of Fuel Characteristics
| Feature | MDO/MGO | LNG |
| Energy density | Higher | Lower |
| Emissions | Higher | Lower |
| Availability | Widespread | More limited in some regions |
| Cost | Generally higher | Can be lower, especially in regions with abundant natural gas |
2. How Do Dual Fuel Marine Engines Work?
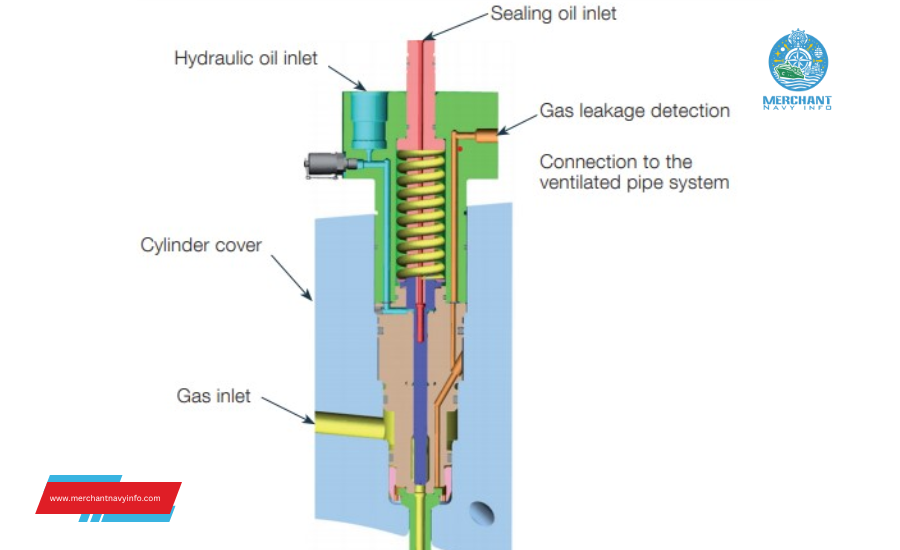
Dual fuel marine engines share a similar design with traditional diesel engines, but incorporate modifications to accommodate the use of LNG. The combustion chamber is designed to burn both liquid and gaseous fuels efficiently, and the fuel injection system is equipped to deliver the appropriate fuel mixture based on the operating mode.
Fuel Management Systems
The fuel management system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of dual fuel engines. It is responsible for:
- Fuel Switching: The system determines when to switch between MDO/MGO and LNG based on various factors, such as engine load, fuel availability, and environmental regulations.
- Fuel Blending: In some cases, the system may blend MDO/MGO and LNG to optimize engine performance and emissions.
- Fuel Injection: The system controls fuel injection into the combustion chamber, ensuring proper mixing with air for efficient combustion.
3. Benefits of Dual Fuel Marine Engines
Environmental Benefits of Dual Fuel Engine
- Reduced Emissions: Dual fuel engines offer significant reductions in sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions, which contribute to air pollution and acid rain. LNG, a cleaner fuel, can substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved Air Quality: By reducing emissions, dual fuel engines contribute to cleaner air in coastal areas and port cities, improving public health and environmental quality.
Economic Benefits for Dual Fuel Engine
- Cost Savings: The ability to switch between fuels based on availability and cost can lead to significant economic benefits. LNG can be a more cost-effective option in regions with abundant natural gas resources than traditional marine fuels.
- Reduced Fuel Consumption: Dual fuel engines can often improve fuel efficiency. Leading to lower operating costs and increased profitability.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Using cleaner fuels can reduce engine wear and tear, leading to lower maintenance costs over time.
Operational Flexibility
- Adaptability to Changing Regulations. Dual fuel engines can be adapted to meet evolving environmental regulations, ensuring compliance with stricter emissions standards.
- Fuel Availability. The ability to operate on both MDO/MGO and LNG provides greater flexibility in terms of fuel availability, especially in regions with limited access to certain fuels.

Regulatory and Compliance Aspects for Dual Fuel Engine
International Regulations
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) plays a crucial role in regulating the maritime industry, including the use of dual fuel marine engines. The IMO has implemented various regulations to address environmental concerns and promote sustainable shipping practices.
Compliance with Sulfur Content Rules and Emission Standards
One of the most significant IMO regulations affecting dual fuel engines is the Global Sulfur Cap. Which limits the sulfur content in marine fuels to 0.50% m/m from 2020 onwards. Dual fuel engines operating on LNG can easily comply with this regulation as LNG has a negligible sulfur content.
Additionally, the IMO has established emission control areas (ECAs) where stricter emission standards apply. In these areas, dual-fuel engines can significantly benefit from reducing emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter.
Regional Regulations
While the IMO sets international standards, individual countries or regions may have additional regulations or requirements for marine vessels operating within their jurisdictions. Ship owners and operators must be aware of and comply with these regional regulations to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations.
Challenges and Considerations for Dual Fuel Engine
Technical Challenges
Despite their numerous benefits, dual fuel marine engines do present some technical challenges:
- Complexity of Engine Design: Integrating dual fuel capabilities into marine engines can increase complexity, requiring specialized design, manufacturing, and maintenance practices.
- Fuel Compatibility and Storage: Ensuring LNG’s compatibility with other onboard systems and its safe storage and handling can be challenging, especially on smaller vessels.
Economic Considerations
- Initial Investment Costs: The initial investment required to retrofit existing vessels or purchase new dual fuel-powered vessels can be substantial. However, the long-term savings from reduced fuel costs and emissions penalties can offset these initial expenses.
- Impact on Vessel Operating Costs: While dual fuel engines can offer fuel cost savings, other factors such as maintenance costs, crew training, and infrastructure requirements should be considered when evaluating a vessel’s overall operating costs.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Successful Implementations
Numerous shipping companies have successfully implemented dual fuel marine engines in their fleets. Case studies have demonstrated the positive impacts of these engines on environmental performance, economic efficiency, and operational flexibility.
Lessons Learned
Through real-world experiences, the industry has gained valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with dual fuel marine engines. Lessons learned include:
- Thorough Planning and Preparation. Careful planning and preparation are essential for a successful implementation, including assessing vessel suitability, addressing infrastructure requirements, and training crew members.
- Risk Management. Identifying and mitigating potential risks, such as fuel supply disruptions or technical issues, is crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of dual fuel operations.
- Continuous Improvement. To maximize benefits and address emerging challenges, ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and optimization of dual fuel engine performance are necessary.
The Future of Dual Fuel Marine Engines
Technological Advancements
The future of dual fuel marine engines is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on:
- Improved Efficiency: Developing more efficient dual fuel engines that can further reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- Fuel Flexibility: Exploring the potential for dual fuel engines to operate on a wider range of fuels, including biofuels and synthetic fuels.
- Automation: Implementing advanced automation technologies to enhance engine control, maintenance, and safety.
Industry Outlook
The adoption of dual fuel marine engines is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by:
- Stricter Environmental Regulations: The increasing pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality will incentivize the adoption of cleaner propulsion technologies.
- Economic Benefits: The potential for cost savings and operational flexibility will make dual fuel engines an attractive option for many shipping companies.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovations in dual fuel engine technology will further enhance their performance and reliability.
Dual fuel marine engines are poised to significantly contribute to a more sustainable and efficient maritime industry. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities presented by this technology, the shipping sector can contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet.
Summary of Key Points
Dual fuel marine engines offer a promising solution to the growing demand for cleaner, more efficient, and cost-effective propulsion systems in the maritime industry. By combining the power of traditional marine fuels with cleaner alternatives like LNG, these engines provide significant benefits, including:
- Reduced emissions: Lower levels of greenhouse gases, sulfur oxides, and nitrogen oxides.
- Improved air quality: Contribution to cleaner air in coastal areas and port cities.
- Economic benefits: Cost savings from using cheaper fuels and reduced fuel consumption.
- Operational flexibility: Ability to switch between fuels based on availability and regulations.
Final Thoughts on Their Impact on the Maritime Industry
Dual fuel marine engines represent a significant advancement in marine propulsion technology. By combining the power and reliability of traditional marine fuels with the environmental benefits of LNG, these engines offer a compelling solution for a more sustainable and efficient maritime industry. As the demand for cleaner and more efficient shipping continues to grow. Dual fuel engines are poised to play a vital role in shaping the future of marine transportation.
The adoption of dual fuel marine engines represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly maritime industry. By embracing this technology, shipping companies can contribute to a cleaner planet, improve air quality, and enhance their operational efficiency. As regulatory pressures and environmental concerns continue to mount, dual fuel engines are poised to become a mainstream choice for marine propulsion.









