
What is the world’s biggest submarine? Typhoon-Class (Type 941- Nuclear-Powered Ballistic Missile Submarines
The nuclear-powered Typhoon ballistic missile submarines are the largest submarines ever built.
- Project type: Ballistic missile submarines
- Operators: Soviet Navy, Russian Navy
- Manufacturers: Severodvinsk
- Depth: 400 meters
- Endurance: 120 days
Overview
Do you know what is the world’s biggest submarine? Typhoon-class submarines can operate even in Arctic waters. Also, Nuclear-powered Typhoon submarines armed with ballistic missiles are built at the Severodvinsk Shipyard. Moreover, Typhoon-class submarines have an endurance of up to 120 days. It can operate even in Arctic waters.
Nuclear-powered Typhoon submarines armed with ballistic missiles are built at the Severodvinsk Shipyard. The Typhoon-class ballistic missile submarines (Project 941 Akula class) are built at the Severodvinsk Shipyard in the White Sea near Arkhangelsk.
The first of six submarines of the class to enter service was Dmitri Donskoy (TK 208) in 1981, followed by TK 202 in 1983, Simbirsk (TK 12) in 1984, TK 13 in 1985, Arkhangelsk (TK 17) in 1987, and Severstal (TK 20) in 1989. The submarines are based at Litsa Guba in the Russian Northern Fleet.
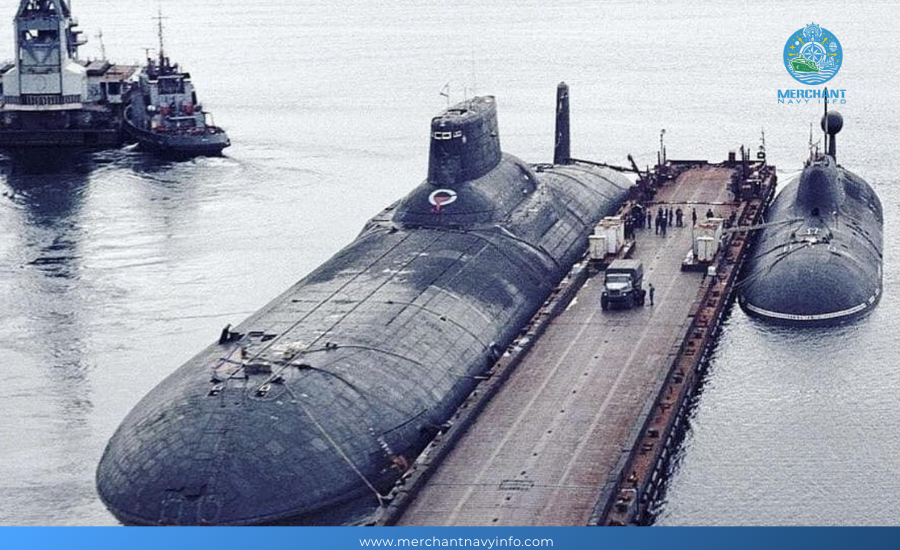
Dmitri Donskoy was relaunched in 2002 after being converted to Project 941UM and used as a test vessel. The submarine was transferred from the Northern Fleet to the Baltic Sea to participate in Kronstadt’s 2017 major naval parade.
Arkhangelsk and Severstal were decommissioned and placed in reserve in 2006 and 2004, respectively. TK 12 and TK 13 have been decommissioned and dismantled.
Also read: How Deep Can A Submarine Go? Find Out Now
The United States, through the Cooperative Threat Reduction Program, assisted in removing the nuclear fuel in TK 202. A US-funded processing facility converted it into a form suitable for long-term storage or reuse. The United Kingdom has agreed to participate in the dismantling of retired Russian nuclear submarines.
Design of the Typhoon-class ballistic nuclear submarine
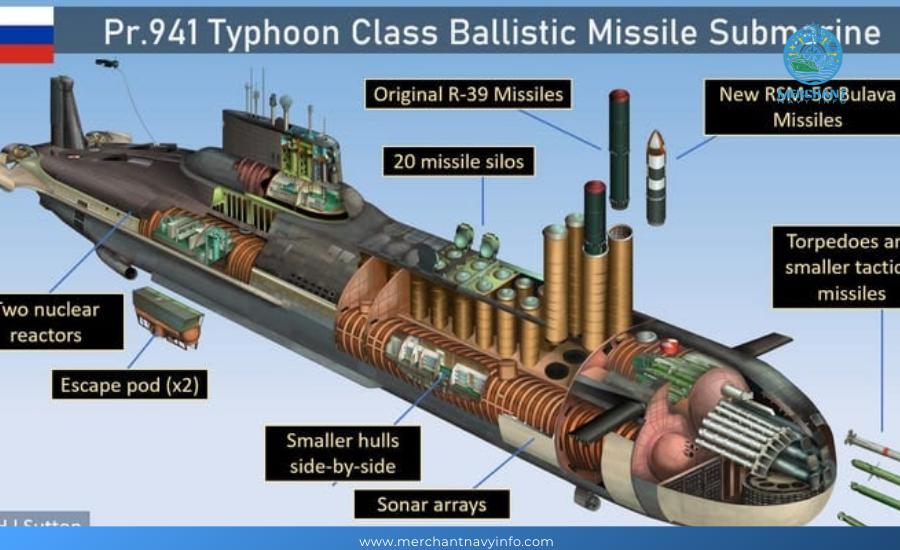
The Typhoon-class submarine adopts a multi-hull design with five inner hulls housed in a superstructure of two parallel main hulls. The superstructure is covered with sound-absorbing tiles. The submarine comprises 19 compartments, including the booster module that houses the main control room and the electronic equipment compartment above the main structure behind the missile launch tubes.
The design of the submarine includes under-ice navigation and icebreaking capabilities. It is equipped with an advanced stern fin and has horizontal hydrogen fins installed behind the screws. The horizontal water fins are located at the front of the submarine and can be retracted into the hull.
The retractable system includes two periscopes (one for the commander and one for general use), a radio rod, radar, radio communications, navigation, and direction-finding masts.
It is located inside the sail shroud. The sail and sail shroud contains a round reinforced icebreaker cover.
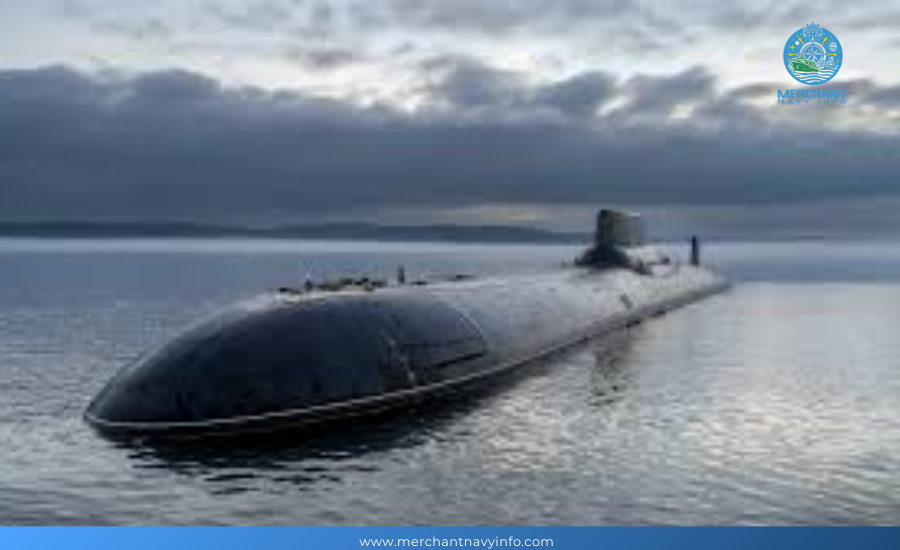

The maximum diving depth is 400 meters. The surfaced speed is 12 kilometers, and the submerged speed is 25 kilometers. The Typhoon submarine can stay at sea for 120 days.
The Typhoon-class missiles from the RSM-52, a three-stage solid-fuel ICBM nuclear submarine. Two rows of missile launch tubes are before the sail between the two main hulls.
Each missile consists of ten independently targetable multiple reentry vehicles equipped with a 100,000-ton nuclear warhead. Inertial guidance with satellite reference update. The range is 8,300 kilometers, and the accuracy (CEP) is 500 meters. The missile weighs 84,000 kg at launch and was designed by the Makayev Design Bureau. Its NATO designation is SS-N-20 Sturgeon.
Also read: How Do Submarines Run Under Water?
In September and December 2005, Dmitry Donskoy successfully conducted flight tests of the new solid-fuel intercontinental ballistic missile SS-N-30 “Bulava” under development for the Russian Navy.
The Bulava missile is said to have a range of more than 8,000 km and can carry a 550-km-power nuclear warhead. It is based on the ground-launched Topol (SS-27) missile. The Russian Navy’s new “Bulava” class submarines are scheduled to be equipped in 2008 and may be equipped with the “Typhoon” class submarines.
Strategic ballistic missile nuclear submarines Typhoon-class torpedoes
The Typhoon has 4 630 mm diameter torpedo tubes and 2 533 mm diameter tubes, comprising 22 different types of anti-submarine missiles and torpedoes. The torpedo room is on the top of the bow between the hulls. The torpedo tubes can also be used to deploy mines.
Typhoon-class strategic ballistic missile nuclear submarine system.
Also read: Biggest Aircraft Carrier – Gerald R. Ford
The sonar is an active/passive search and attack type, and the sonar is installed on the hull below the torpedo room. The submarine has a radar detecting surface targets within the I/J range.

Countermeasures include electronic support measures, radar early warning systems, and direction-finding systems.
The submarine has radio and satellite communication systems. It has two floating antennas for receiving radio signals, target acquisition data, and satellite navigation signals at depth and under ice cover.
Typhoon-class ballistic missile submarine propulsion system
The submarine’s main mechanism consists of two nuclear water reactors and two sets of turbine gearboxes, including steam turbines and gearboxes. A reactor and a set of turbine reducers are installed in each main hull.
Also read: How Deep can a Submarine Dive?
Each nuclear water reactor generates 190 megawatts of electricity. These engines power two 50,000-horsepower steam turbines and four 3,200-kilowatt turbine generators. Two 800-kW diesel generators serve as backup propulsion devices and are connected to the axles. The two propellers are seven-blade fixed propellers. The bow and stern joint propulsion is a rotating retractable propeller rudder driven by a 750-kilowatt motor.









