Maritime transportation is essential to our daily lives as it benefits everyone around the world. Although the development of the aviation industry. Has enabled the movement of people and goods more quickly. The shipping industry remains vital to economic growth. The backbone of international trade, freight transport allows tons of goods. From toys to trucks, to move across vast, eternal oceans every day. According to the International Chamber of Shipping. The shipping industry handles nearly 90% of world trade, with more than 50,000 merchant ships serving internationally. So learn the suez canal definition.
However, not only the various natural bodies that make international maritime trade. Possible but also various human interventions in maritime transport have enhanced the global movement of people and goods. Man-made canals around the world have transformed international shipping by shortening shipping routes and reducing operating costs. Major man-made canals, such as the Panama Canal, Volgadon Canal, and Corinth Canal. Grand Canal, and Suez Canal, provide alternative transport routes to the world’s major saltwater networks and enable efficient maritime transport.
Where is the Suez Canal?
The 193.30 km (120 mi) long Suez Canal definition,is an artificial waterway in Egypt. That connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Gulf of Suez, a northern tributary of the Red Sea. Officially opened in November 1869, the Suez Canal is one of the world’s busiest shipping lanes. With thousands of ships passing through it each year. The canal separating the continents of Asia and Africa. Provides the shortest shipping route between Europe and the regions bordering the Indian and Western Pacific Oceans. The journey from Europe via the Suez canal definition, through the Mediterranean. And the Red Sea is approximately 7,000 kilometers shorter. Then the journey through the South Atlantic and South Indian Oceans. The canal also connects Port Said in northeastern Egypt with Port Toufik in the city of Suez in the south.
Built
Suez Canal was built between 1859 and 1869 by the Suez canal definition, Company, which owned and maintained the waterway. In 2015, Egypt completed a major expansion of the Suez Canal. Deepening sections of the canal and constructing a 35 km second channel along part of the main waterway. The expansion allowed the canal to accommodate traffic in both directions and larger ships on parts of the route. In December 2017, the world’s largest container ship. The OOCL Hong Kong, with a total length of 400 meters, passed through the Suez Canal carrying 21,400 containers.
The canal plays an important role in the growth of Egypt’s economy. As it handles approximately 8% of the world’s seaborne trade annually. According to Reuters, the Suez Canal generated $5.3 billion in revenue in 2017. Although the Suez Canal was not officially completed until 1869, it has a long history of connecting Egypt’s Nile River and the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
History
The history of the Suez Canal dates back to approximately 40 centuries. During the time of the ancient Egyptian pharaohs, the idea of connecting the Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea arose. The concept of a canal linking these seas with the Nile River was developed during the reign of the Egyptian pharaoh Senausret III (1887-1849 BC), when the first canal in the region connecting the two seas through the Nile River was constructed. It lasted until. However, canals often remained abandoned for years after construction.
At the same time, the canal was under various rulers, including City I (1310 BC), Necho II (610 BC), King Darius of Persia (522 BC), and Emperor Trajan (117 AD). Yes, it has opened several times. For shipping. Amro ibn Elas (640 AD) and others. Historical documents indicate that the canal was expanded, and several other attempts were made to build new canals during this period. The first modern attempt to build a canal was made in the late 18th century during Napoleon’s Bonaparte campaign in Egypt.
Construction
He said that the construction of a French-controlled canal across the Isthmus of Suez would create trade problems for Britain, as Britain would have to either pay duties to France or continue transporting goods overland or around southern Africa. Research into Napoleon’s canal plans began in 1799 year. However, due to a measurement error, the difference in sea level between the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea proved too great for the construction of the canal, and construction was immediately halted.
With the rise of new Europe and the development of industry and maritime trade, entrepreneurs began thinking about building canals. One such plan was to connect the Red Sea directly to the Mediterranean, saving time in circumnavigating Africa and transshipping cargo and passengers via the Suez Peninsula.
The next attempt to build a canal in the area occurred in the mid-19th century when French diplomat and engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps persuaded the Egyptian governor Said Pasha to support the construction of a canal. In 1858, the Compagnie Universelle du Canal Maritime de Suez was founded, and the canal was constructed, for which he was given the right to operate for 99 years. The Egyptian government would then take control of the canal.
How Do Ships Navigate the Suez Canal?
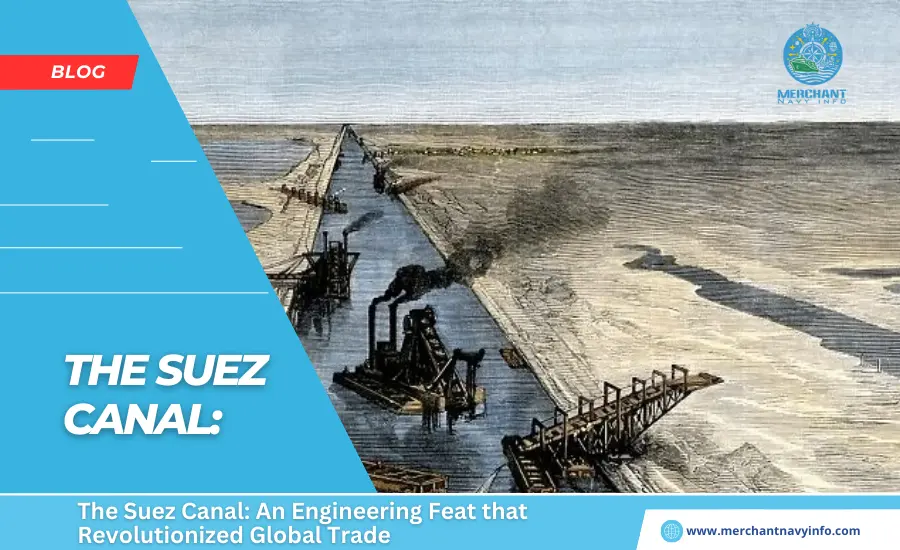
Construction of the Suez Canal
In addition, the original total cost of the project was estimated at 200 million francs. However, the decision to build a canal connecting the Mediterranean and the Red Seas provoked criticism from Britain, which saw the project as a political project to weaken the country’s dominance in maritime trade. Britain continued to oppose the project until the Empire purchased its 44 percent stake in the canal after the Egyptian government auctioned off its stake in the canal in 1875, citing financial problems. The construction of the canal was initially carried out by forced labor. It is said that thousands of people were forced to use picks and shovels to dig canals until the Pasha banned forced labour in the 1863 year.
This forced the Suez Canal Company to introduce custom-built steam and coal-powered shovels and excavators to build the canal. With the help of this machine, the project gained the necessary impetus, and on November 17, 1869, it became possible to channel the waters of the Mediterranean through the canal into the Red Sea. When the Suez Canal was made navigable, it was 200 tons long, 300 feet wide at the surface, 72 feet wide at the bottom, and 25 feet deep. Upon completion, the total cost of the project was more than double his original estimate.
Suez Canal and Political Crisis
After the project’s completion, the Suez Canal had a major impact on world trade, but traffic on the waterway initially fell short of expectations. Meanwhile, financial problems related to the construction of the canal led the British government to buy out her stake in the Egyptian interests in 1875, making her a major shareholder in the Suez Canal Company. The canal was vital to the British economy as it provided a short route to the colonies and the oil fields of the Persian Gulf. Britain tightened its control when Egypt went bankrupt in 1875, allowing European banks to take control of the country’s finances. This angered the Egyptians as France and England continued to take control of the country. This led Britain to invade Egypt in 1882. Egypt remained de facto independent under her 1936 Anglo-Egyptian Treaty, but Britain assumed full control of the Suez Canal.
During World War I
Britain declared Egypt a protectorate and sent troops to protect the canal. This continued until 1922, when Britain granted Egypt nominal independence. In 1936, the Anglo-Egyptian Treaty declared Egypt a sovereign state, but it was not until 1956 that Britain agreed to withdraw its troops from Egypt. Massive political unrest over the Suez Canal, known as the Suez Crisis, began in July 1956 when then-Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal and closed the Strait of Tiran. This decision began the invasion of Egypt by Britain, France, and Israel. Only after UN intervention did her three forces withdraw from Egypt, allowing Egypt to reopen the canal to commercial shipping. However, political instability lasted a long, and Egyptian authorities closed the canal in 1967 during the Six-Day War between Israel and Egypt.
Canal Closure
Has left her 15 ships stranded in the middle of the Great Bitter Lake canal. These ships, known as the Yellow Fleet, remained trapped until 1975 when Egypt reopened the Suez longest canal in the world following peace negotiations with Israel. Since then, the suez canal definition has remained an important shipping link between the Mediterranean and the Red Sea, allowing international ships to avoid problematic passages around the southern tip of Africa. According to the Suez Canal Authority, the world’s longest canal in the world without locks is expected to have an average daily capacity of 97 ships and revenue of $13.226 billion by 2023.










